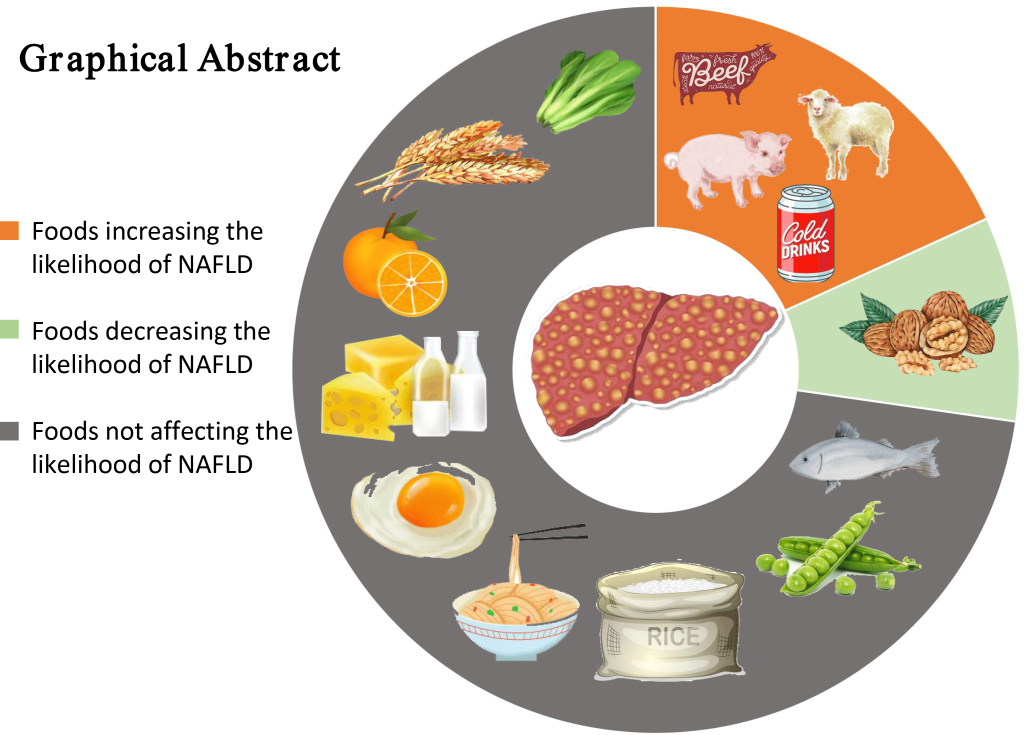
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a medical condition that is becoming increasingly common in modern society. It is estimated that 25% of the global population has NAFLD, making it the most common liver disease in the world (1)
NAFLD is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver of individuals who consume little or no alcohol. Although the condition is often benign, in some cases, it can progress to more severe forms of liver disease, including cirrhosis and liver cancer.
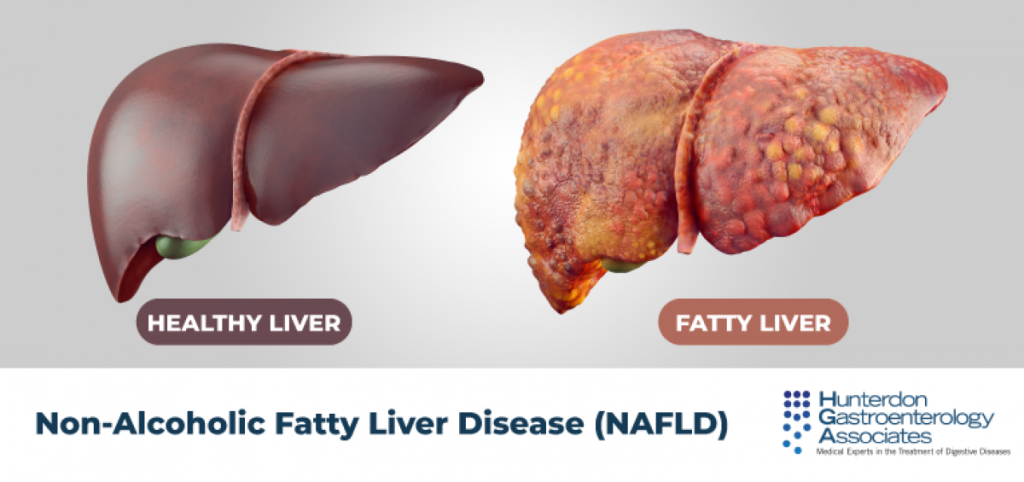
What Causes NAFLD?
The exact causes of NAFLD are not well understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. These include:
- Obesity: Obesity is one of the most significant risk factors for NAFLD. Individuals who are overweight or obese are more likely to develop the condition.
- Insulin resistance: Insulin resistance is a condition in which the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance is associated with an increased risk of NAFLD.
- High levels of triglycerides: High levels of triglycerides in the blood are also associated with an increased risk of NAFLD.
- Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels. People with type 2 diabetes are at an increased risk of developing NAFLD.
- Genetics: Some people may be more susceptible to developing NAFLD due to genetic factors.
According to a latest research NAFLD has a different trigger for fat deposits in the liver: a group of metabolic risk factors. NAFLD is most common in people who have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, insulin resistance (prediabetes), or type 2 diabetes. It is also common among people who are overweight or obese, though it is possible to develop NAFLD even if your body mass index (BMI) is normal. (2).
Symptoms of NAFLD
Many people with NAFLD do not experience any symptoms. However, in some cases, the following symptoms may be present:
- Fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort
- Enlarged liver
- Elevated liver enzymes in blood tests
Diagnosis and Treatment of NAFLD
NAFLD is usually diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies, and a liver biopsy. If NAFLD is diagnosed, treatment may involve lifestyle changes such as weight loss, dietary changes, and increased physical activity. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage underlying conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol.
Prevention of NAFLD
NAFLD can often be prevented through healthy lifestyle habits such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise. Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption is also important, as alcohol can cause liver damage and increase the risk of developing NAFLD.
The following are some lifestyle changes that can help prevent or reduce the risk of developing NAFLD:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for NAFLD. Losing weight through a healthy diet and exercise can reduce the amount of fat in the liver and decrease the risk of developing NAFLD (4).
- Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation, and promote weight loss. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Eat a healthy diet: A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce the risk of developing NAFLD (3). health.
- Avoid alcohol: Alcohol can contribute to liver damage and should be avoided or consumed in moderation.
- Avoid fast food: Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated fats can also help. A recent study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology linked regular fast-food consumption (20% or more of total daily calories) with fatty liver disease — especially in people who had type 2 diabetes or obesity. Fast foods tend to be high in saturated fats, added sugar, and other ingredients that affect metabolic
- Switch your soft drinks with more healthy drinks: Soft drinks with high-fructose corn syrup, or other sugar-sweetened beverages, lead directly to large increases in liver fat deposits, independent of the total calories consumed. Read labels closely for added sugars, including corn syrup, dextrose, honey, and agave. Instead of sugary drinks, sip plain water. Black coffee or with a splash of cream is also a good pick; research suggests coffee has the potential to decrease liver scarring (5).
- Manage underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol can increase the risk of NAFLD. Properly managing these conditions through medication and lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk.
- Avoid unnecessary medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and tamoxifen, can contribute to liver damage and should be avoided unless necessary and under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
It’s important to note that if you already have NAFLD, these lifestyle changes may help slow or even reverse the progression of the disease. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations and treatment options.
In conclusion, NAFLD is a common liver disease that can be prevented through healthy lifestyle habits. If you are at risk of developing NAFLD or are experiencing symptoms, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28930295/
https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/a-practical-guide-to-the-mediterranean-diet-2019032116194
