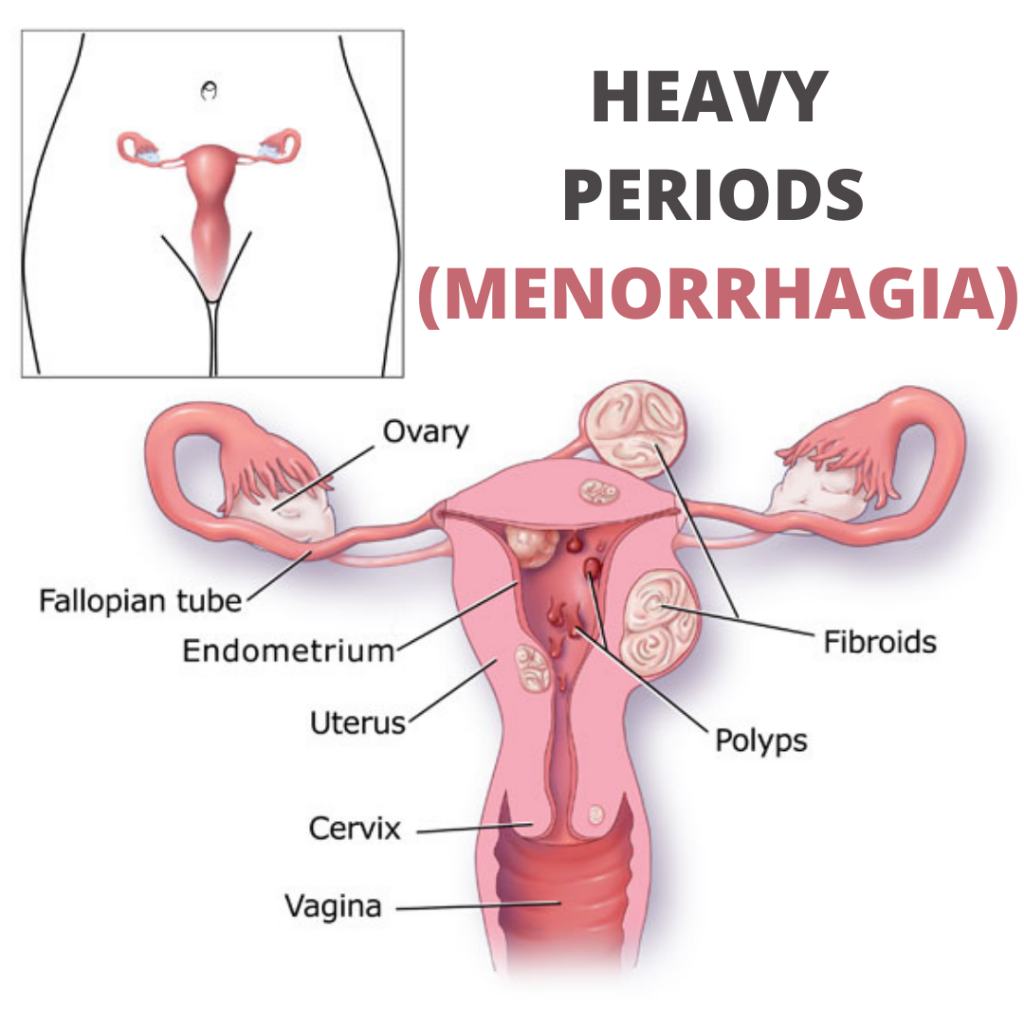
WHAT IS MENORRHAGIA?
Menorrhagia means unusually heavy periods or bleeding between periods, Women with menorrhagia may experience ‘flooding’, may pass large clots with the menses, And it may have periods that are prolonged (lasting more than 7 days).
- Normal period blood loss is between 20 to 60 mL (4 to 12 teaspoonfuls).
- The average blood loss in a menstrual cycle is 30 to 40 mL.
- A heavy period of blood loss is more than 80 mL (half a teacup).
It is a common complaint affecting 5 to 10% of women.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Apart from heavy blood loss during the period and bleeding or spotting between periods.
There may be cramping pains in the lower abdomen. Heavy bleeding may be described as ‘saturated pads’, ‘frequent changing’, ‘accidents’, and ‘clots’.
There may be prolonged bleeding.
Since there is a risk of iron deficiency, symptoms of anemia such as fatigue and weakness may occur.
WHAT ARE CAUSES?
In most cases the exact cause is unknown and the uterus (womb) and ovaries appear normal—this is called ‘dysfunctional uterine bleeding’. It is most common at the extremes of reproductive age—menarche and menopause.
We do know that a chemical called prostaglandin is a factor since its level in the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) is high in women with heavy periods and tends to stop the clotting of blood.
KNOWN CAUSES INCLUDE:
- fibroids, which are non-cancerous growths in the muscle of the uterus
- hormone contraceptives including Depo Provera
- endometriosis of the uterus
- the intrauterine device (IUD)—a contraceptive device placed in the uterus
- bleeding disorders and warfarin used to reduce blood clotting
- miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy
- infection, including sexually transmitted infection
- endometrial cancer in the lining of the uterus.
HOW MENORRHAGIA IS DIAGNOSED?
Apart from a thorough clinical examination by your doctor including a pelvic examination and Pap test, some of the following tests may be ordered:
- blood tests to check for anemia
- abdominal and vaginal ultrasound
- endometrial biopsy
- D & C (dilatation and curettage)
- Hysteroscopy, where a ‘telescope’ is placed inside the uterus for inspection
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
SURGICAL TREATMENT
- D & C to gently scrape away the endometrium
- Total removal of the endometrium
- Surgery to remove tumors such as fibroids and polyps
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus), which is the last resort if all other options including more limited surgery
- have not worked
TREATMENT OF DYSFUNCTIONAL BLEEDING
In this category, there is no clear-cut cause so the aim of treatment is to reduce the amount of blood loss.
This is done by giving hormone treatment (progesterone) or anti-prostaglandin medication such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or by helping blood clotting and reducing bleeding (tranexamic acid).
If the doctor and the patient agree that the heavy periods do not interfere too much with life.
A decision can be made to live with the problem but monitor it,
including checking for anemia.
EXAMPLES OF TREATMENT ARE:
- The oral contraceptive pill. This is an important treatment as it reduces bleeding by one-third.
- Progesterone tablets. These are excellent, especially for acute heavy bleeding.
- Progesterone-releasing IUD. This device (Mirena) releases hormone gradually and makes the lining of the uterus very thin. It also acts as a contraceptive.
- Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron). This is the most effective therapy, reducing bleeding by almost half. The tablets should be taken four times a day for 4 days.
NOTE:
- Keep a menstrual diary.
- Rest as much as possible.
- Take iron supplements (best to have blood tests first).
- Eat a well-balanced diet.
- Avoid aspirin (may increase bleeding).
