
After a miscarriage, you will undoubtedly be confused and wondering why this sad event happened to you. The main thing is to remember that it was nothing that you did wrong, and so you should not feel any sense of blame or guilt.
WHAT IS MISCARRIAGE?
A miscarriage, which is called a spontaneous abortion in medical terms, is the spontaneous ending of pregnancy before the baby (fetus) can survive outside the womb. This is usually considered to be up to the 20th week. A loss after this time is called a stillbirth. Sometimes it is complete (when both fetus and afterbirth are expelled); sometimes it is incomplete (when only part of the pregnancy is expelled).
WHAT ARE THE SURPRISING FACTS?
- About 1 in 4 pregnancies are ‘lost’ (i.e. miscarried).
- Many are lost soon after conception; in such a case the woman may not be aware of anything except a small alteration in her period.
- In most cases, the fetus is lost in the first 12 weeks and is obvious to the mother.
WHAT ARE SYMPTOMS?
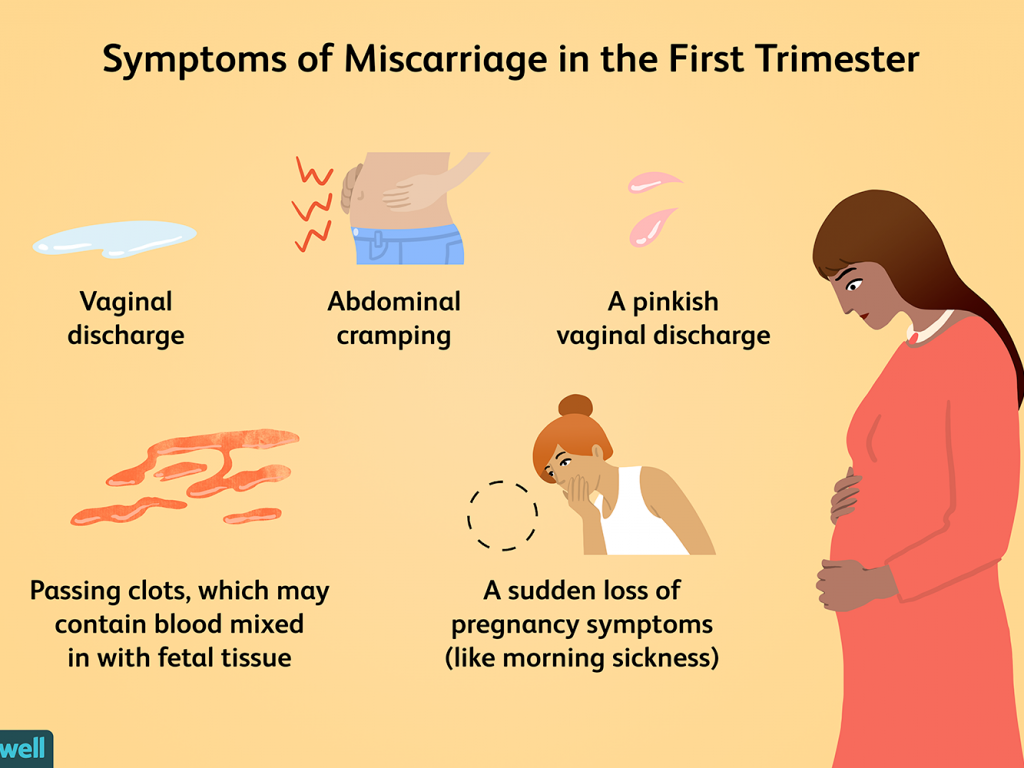
The first symptom is the loss of blood from the vagina, which can vary from slight to heavy flow. At this stage, it is called a threatened miscarriage. When the solid products are passed, you feel pain due to cramping of the uterus. It is usual for only some parts to be passed to the outside, while others (e.g. the afterbirth) stay behind. This is referred to as an incomplete miscarriage or abortion. However, if the miscarriage is later in the pregnancy (such as at 20 weeks), it is more usual to have a complete abortion.
WHAT IS THE CAUSE OF MISCARRIAGE?

Most miscarriages occur without an obvious cause. However, in many, there is something wrong with the developing fetus, and a miscarriage is nature’s way of handling the problem.
This abnormality may be caused by a genetic disorder, or by a viral infection that has affected the fetus in the first 12 weeks. Often the mother is unaware that she has picked up a serious infection (such as rubella, influenza, or cytomegalovirus), but it is harmful to the delicate growing tissues of the fetus.
In other cases, abnormalities of the uterus may not allow the fertilized egg to attach to its lining, or it may reject the developing fetus later on. The mother may also have a clotting disorder of the blood
BLIGHTED OVUM
This occurs when a pregnancy sac is formed in the uterus but there is no developing baby and the sac is expelled. It is a common cause of miscarriage.
WHAT ARE RISKS?
There is usually no risk to the mother’s health. However, if the miscarriage is incomplete and not treated, infection or anemia from blood loss could occur. If you get a fever, heavy bleeding, severe pain, or an offensive discharge, contact your doctor. After a miscarriage, you may feel emotionally upset or depressed, with feelings of loss and grief. If so, you will require help.
WILL IT HAPPEN AGAIN?
Having a miscarriage doesn’t make it any more likely you will have another miscarriage. The odds favor your next pregnancy being successful. There is no special treatment to prevent any further miscarriages, and it is best left to nature to take its course. However, it is advisable to keep healthy and not indulge in alcohol, smoking, or the use of other drugs.
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT?
It is usual to have a surgical ‘cleaning’ of your uterus, especially if the miscarriage was early in the pregnancy and bleeding continues. This is called a dilation and curettage (D&C). However, many women, in consultation with their doctor, choose to ‘let nature take its course’ and let it resolve by itself. The bleeding may then stop in a few days. If it persists, a D&C is then an option.
Other aspects of treatment include:
- basic pain medication such as paracetamol
- blood tests and possible ultrasound examination
- checking for Rhesus blood grouping (a Rhesus-negative person may be given immunoglobulin)
- reduced activity and rest for at least 48 hours.
Pay attention to any adverse emotional reactions—make sure you talk about any unusual feelings. Talk over your feelings with your partner and family. You will need at least a week off work
HOW SOON WILL WAIT BEFORE TRYING AGAIN?
You can safely start trying to get pregnant again very soon. It is best to wait until you have had at least one normal period. Your next period may be heavy and abnormal. Use sanitary towels and not tampons for the next 4 weeks.
Make sure that your body is ready before having sex again. It usually takes a while to become interested in sex again, and therefore partners have to be very patient and understanding.
